Search our Grants
MDA’s research program awards grants to the world’s best scientists investigating promising theories and therapies that may accelerate treatments and cures for families living with muscular dystrophy, ALS and related neuromuscular diseases.
Grant - Summer 2012 - ALS — Christine Vande Velde, Ph.D.
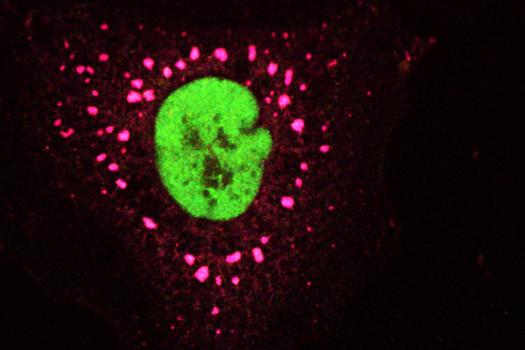
MDA awarded a research grant totaling $358,242 over three years to Christine Vande Velde, research assistant professor in the department of medicine at the University of Montreal Hospital Research Center in Montreal, Quebec (Canada). The funds will help support Vande Velde’s study of the role of TDP43 and the stress granule mechanism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Vande Velde and colleagues are looking at the interplay between genetic susceptibility and environmental exposures to toxins that are thought to be relevant in ALS. It’s known that cells exercise a variety of mechanisms to mediate recovery following exposure to environmental stress, one of which is the formation of proteins and RNA molecules into clumps called stress granules.
In previous work, Vande Velde’s team has indicated that TDP43 plays an important role in stress granule formation.
“In particular, this grant focuses on TDP43 and its regulation of an important cell survival mechanism: the formation of stress granules,” Vande Velde explains. Her team will use a combination of cellular and rodent models to dissect the stress granule mechanism in which TDP43 operates and determine the impact of ALS-causing mutations on this pathway.
“This is an exciting area for ALS research,” Vande Velde says, “as demonstrated by a recent convergence on this topic by many groups.”
Funding for this MDA grant began Aug. 1, 2012.
Grantee: ALS — Christine Vande Velde, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Spring 2014 - ALS - Aaron Gitler, Ph.D.

Aaron Gitler, an associate professor of genetics at Stanford University in Stanford, Calif., was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $253,800 over three years to investigate how mutations in the gene for a protein called profilin 1 cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
In experiments conducted in cells, Gitler and colleagues have found that the profilin 1 protein may be a regulator of "stress granules" — tiny cellular factories that stores and process RNA molecules — and that further understanding this function may provide insights that lead to ALS therapy development.
Funding for this MDA grant began May 1, 2014.
Grantee: ALS - Aaron Gitler, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Summer 2013 - CCD — Kurt Beam, Ph.D.

Kurt Beam, professor of physiology and biophysics at the University of Colorado at Denver, was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $300,000 over a period of three years to study two proteins that, when they malfunction, cause central core disease (CCD).
Muscle contraction in response to a nerve signal involves the interaction of two proteins: the dihydropyridine receptor (DHPR), which “senses” the electrical signal, and the ryanodine receptor (RyR1), which controls the release of calcium ions. Mutations in either one lead to CCD, as well as other muscle disorders. Beam will introduce the genes for these proteins into mouse muscle and nonmuscle cells. For both cell types, he says, researchers will measure the tiny electrical currents (less than a billionth of an ampere) produced by the DHPR. Fluorescence microscopy and calcium indicator dyes will be used to monitor movements of calcium inside individual cells; and confocal microscopy used to determine whether DHPRs and RyR1s are close to one another in the cells. The structure of these proteins then will be analyzed at a higher resolution by means of electron microscopy.
“Using these techniques, we hope to identify exactly what parts of the two proteins touch one another,” and how these sites of interaction and the overall shapes of the two proteins are affected by disease-causing mutations, Beam says.
“Although we have known for upward of 20 years that the DHPR and RyR1 are crucial for muscle contraction, we still do not understand the mechanism of their interaction, or exactly how disease-causing mutations affect this interaction,” says Beam. His research will attempt to better understand those interactions in order to define possible therapeutic targets for CCD and related muscle diseases.
Funding for this MDA grant began August 1, 2013.
Grantee: CCD — Kurt Beam, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Additional Grants 2012 - ALS — NeuRx Diaphragm Pacing System (DPS)
The Muscular Dystrophy Association has committed $750,000 to help support a phase 2 clinical trial assessing the ability of the NeuRx Diaphragm Pacing System (DPS) to improve respiratory function and quality of life in people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Developed by Synapse Biomedical in Oberlin, Ohio, the DPS received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on Sept. 29, 2011, as a “humanitarian use device” (HUD) for the treatment of chronic hypoventilation (inadequate breathing) in ALS. The surgically implanted device stimulates the movement of the diaphragm, the main muscle used in breathing.
In people with ALS who have chronic breathing problems and whose diaphragms are still able to respond to electrical stimulation, the DPS may forestall or negate the need for invasive ventilation.
Investigators will compare respiratory function and quality of life in people with ALS who use the DPS and those who receive the current standard treatment.
Grantee: ALS — NeuRx Diaphragm Pacing System (DPS)
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant – Winter 2013 – CMT - Vera Fridman, M.D.

Vera Fridman, at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, was awarded an MDA clinical research training grant totaling $180,000 over a period of two years to the effects of Serine in people with a form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease called hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1 (HSAN1).
CMT is the most commonly inherited neurological disorder, affecting 1 in 2,500 people worldwide. It is a slowly progressive disorder, causing degeneration of the peripheral nerves that control sensory information coming from the limbs. HSAN is a rare genetic neuropathy that causes severe numbness, weakness and ulceration of the feet and hands.
Two abnormal lipids (fat-like substances) have been identified in the blood of both humans and mice with HSAN1. It has been shown that levels of these lipids can be reduced by administering the amino acid serine, and that mice treated with serine have better motor and sensory function.
Fridman’s goal is to determine the effect of serine on symptoms of people with HSAN1 in order to assess whether serine supplementation may be an effective therapy for the disease.
Funding for this MDA grant is effective July 1, 2013.
Grantee: CMT - Vera Fridman, M.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Summer 2013 - CCD — Julio Vergara, Ph.D.
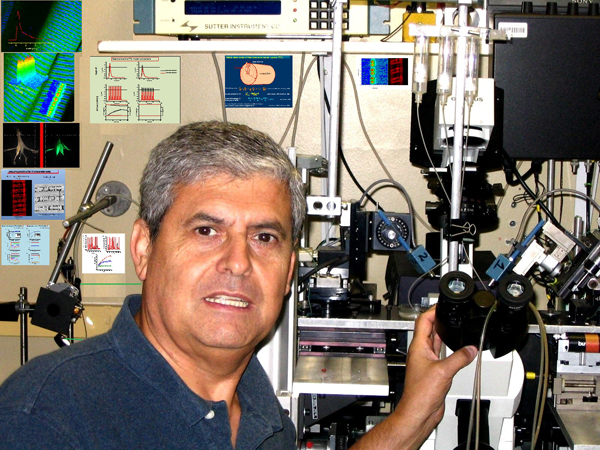

Julio Vergara, professor of physiology at the University of California, Los Angeles, was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $300,000 over a period of three years to study the basis of central core disease (CCD).
CCD is an inherited muscle disease that causes poor muscle tone and weakness, susceptibility to heat-related illnesses, and a risk of malignant hyperthermia, a dangerous reaction to certain anesthetic drugs. One cause of CCD is a defect in a muscle protein called the type 1 ryanodine receptor, which regulates the releases of stored calcium in the muscle. This release of calcium is critical for normal muscle contraction.
Much remains to be understood about the connections between CCD and alterations in the ryanodine receptor, Vergara says. His work will pursue these connections in mice carrying the mutant gene.
“Our research aims to answer the following questions,” Vergara explains. “Why do mutated receptors predispose muscle fibers to triggering agents that lead to fulminant [sudden, rapid, severe] malignant hyperthermia episodes? And, how does dantrolene, a commonly used drug, prevent fulminant MH episodes?”
He will investigate these issues using a combination of state-of-the art optical and electrophysiological approaches in adult muscle fibers from animal models, and comparing calcium release among mice with different mutations in the receptor gene.
“The mice have become a great tool to investigate the molecular and pathophysiological alterations underlying the mysteriously intertwined malignant hyperthermia/CCD human pathology,” Vergara says.
Funding for this MDA grant began August 1, 2013.
Grantee: CCD — Julio Vergara, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant – Winter 2013 – CMT - Ronald K. Liem, Ph.D.
Ronald Liem, professor of pathology and cell biology at Columbia University Medical Center in New York, N.Y., was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $318,264 over a period of three years to study the progression of disease in a mouse model of type 2E Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease.
CMT is the most commonly inherited neurological disorder, affecting 1 in 2,500 people worldwide. It is a slowly progressive disorder, causing degeneration of the peripheral nerves that control sensory information coming from the limbs. CMT2E is caused by mutations in the gene for a protein called neuronal intermediate filament light (NFL). NFL provides stability to axons, the long extensions of muscle-controlling motor nerve cells called motor neurons that allow them to control muscle contractions.
Liem’s lab has created a mouse model of CMT2E by introducing a mutated copy of the gene. Their preliminary results indicate the mouse develops many of the same features as people with the disease, including deficits of movement and hearing. “We believe that this new mouse model is likely the best model of CMT type 2E and will allow us to study the progression of the disease at a level that is not possible in human subjects. We expect that the mouse model will also be useful for testing therapeutic compounds when they become available,” Liem says.
Liem will be performing detailed developmental and anatomic studies to follow the progression of the disease in mice, and to learn more about exactly how the mutation causes problems. One focus will be on the effects of the mutation on mitochondria, the cell’s "powerhouses," which are believed to be involved in CMT.
“These studies will give us a better understanding of the mechanisms by which nerve damage occurs as a result of this mutation,” Liem says. “We expect that the mouse model also will be useful for testing therapeutic compounds when they become available.”
Funding for this MDA grant began Feb. 1, 2013.
Grantee: CMT - Ronald K. Liem, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Additional Grants 2012 - ALS — Bridge-to-Industry Training Program
MDA launched its innovative Bridge-to-Industry (B2I) program with a $180,000 grant over three years to postdoctoral fellow Archi Joardar at the University of Arizona in Tucson, to develop two promising drug candidates for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
MDA’s Bridge-to-Industry, or B2I, is a pilot project that trains promising researchers in translational research by providing experience both in academia and the biopharmaceutical industry.
Through the B2I program, MDA is able to fund investigators to conduct drug development research under the guidance of two mentors: one experienced in academic research and the other experienced in the industrial side of drug development.
Daniela Zarnescu, associate professor in neuroscience and molecular & cellular biology at the College of Science, University of Arizona (UA), will provide academic mentoring to Joardar. Zarnescu currently has an active MDA research grant for her work on gene and drug discovery research in a fruit fly model that carries a mutation in the ALS-associated TDP43 gene.
Joardar will receive mentoring on the industry side from Chris Hulme, co-director of the BIO5 Institute in Oro Valley, Ariz. Hulme is an expert in small-molecule drug design and the development of chemical-based methods to hasten the drug discovery process.
Mentorship under Zarnescu and Hulme will provide Joardar with a unique environment in which to train while furthering the development of two promising ALS drug candidates identified in Zarnescu's work. Joardar will evaluate the ability of each drug to reduce neurotoxicity caused by ALS-associated mutations in the TDP43 gene..
Grantee: ALS — Bridge-to-Industry Training Program
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Summer 2012 - ALS — Alex Parker, Ph.D.

MDA awarded a research grant totaling $231,300 over three years to Alex Parker, assistant professor in the department of pathology and cellular biology at the University of Montreal Hospital Research Center in Montreal, Quebec (Canada). The funds will help support Parker's study of cellular stress response in neurodegeneration associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Mutations in the genes for TDP43 and FUS proteins have been linked to ALS, Parker notes, "and they cause persistent cellular stress that ultimately overwhelms the neuron’s [nerve cell's] coping mechanisms, leading to cell death."
With colleagues, Parker is working to better understand a critical cell survival mechanism known as the endoplasmic reticulum stress response, which is known to reduce the toxicity caused by mutant TDP43 and FUS proteins. (The endoplasmic reticulum is a cellular compartment involved in the transport of proteins and other biological substances within cells.)
Using a C. elegans (nematode, or roundworm) model of ALS, Parker aims to identify small molecules that modify the ER stress response to help neurons overcome protein toxicity and stave off cell death.
Parker's work potentially could led to the identification of therapeutic targets and development of therapies for people with ALS.
"There are very few drugs available to treat neurodegeneration, and they are not very effective," Parker says. "We hope our findings accelerate drug discovery and development for ALS patients."
Funding for this MDA grant began Aug. 1, 2012.
Grantee: ALS — Alex Parker, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant – Winter 2013 – CMS - Michael Linhoff, Ph.D.
Michael Linhoff, a postdoctoral fellow at Oregon Health and Science University in Portland, Ore., was awarded an MDA development grant totaling $119,944 over a period of two years to study neuromuscular junction defects in congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS).
A common cause of CMS is mutation of the RAPSN gene. This gene encodes a protein, rapsyn, that helps other proteins assemble properly on the surface of the muscle at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). The NMJ is where the motor neuron from the nervous system contacts the muscle. The neuron releases chemicals that cause the muscle to contract.
Linhoff and colleagues have shown that a RAPSN mutation causes defects not only on the muscle, but also on the neuron where it contacts the muscle. Mutation reduces the effectiveness with which the neuron releases its chemicals, reducing muscle contraction and causing weakness.
He is studying this effect in zebrafish, a well-characterized lab model for the study of the interaction between nerve and muscle. “Our lab previously identified a mutant fish line [with a mutation in the RAPSN gene], called twitch once, that exhibits use-dependent fatigue similar to patients with CMS,” Linhoff says.
He will be using high-resolution imaging technologies to study the mechanisms underlying the dysfunctions seen in the twitch once fish. Using the images, he will develop three-dimensional models of the zebrafish neuromuscular junction to discover the details of the neuronal defect caused by the mutation.
“Determining the molecular mechanisms underlying this dysfunction may yield potential therapeutic targets to correct use-dependent fatigue in patients with congenital myasthenias,” Linhoff says.
Funding for this MDA grant began Feb. 1, 2013.
Grantee: CMS - Michael Linhoff, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant – Winter 2013 – CMD, LGMD - Sebahattin Cirak, M.D.
Sebahattin Cirak, pending assistant professor at the Children’s National Medical Center in Washington, D.C., was awarded an MDA development grant totaling $180,000 over a period of three years to hunt for elusive genes that cause congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) and limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD).
Though CMD and LGMD are different diseases, they are similar in one respect: Both can be caused by a variety of different mutations in the same gene, and about half the time, the causative mutations are unknown.
New mutation hunting techniques have become available in the past several years that allow researchers to find gene mutations by examining the gene’s “messenger,” called RNA. Genes carry the instructions for making a new protein. To do so, a gene creates a “working copy” of itself using RNA. By carefully analyzing that RNA with a variety of techniques, it is possible to discover new gene mutations.
Cirak will use RNA extracted from muscle biopsies of people with CMD or LGMD. “I hope to uncover these elusive mutations by studying RNA, using the latest available sequencing technology,” he says.
“This research will improve the methods for molecular diagnostics of the muscular dystrophies,” he adds, with the goal of providing more families with the knowledge of the cause of their disease. In addition, the discovery of new genes can reveal new information about the exact causes of the disease, potentially suggesting new avenues for developing treatments.
Funding for this MDA grant began Feb. 1, 2013.
Grantee: CMD, LGMD - Sebahattin Cirak, M.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant – Winter 2013 – BMD, DMD - Linda Baum, M.D., Ph.D.
Linda Baum, professor and vice chair of pathology and laboratory medicine at the Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $405,000 over a period of three years to study molecules on the muscle surface that regulate important aspects of cellular communication and survival.
All cells, including muscle cells, are coated with an elaborate set of molecules called glycoproteins. These perform multiple critical functions, including: attaching cells to one another, relaying messages between cells, and ultimately, helping the cell survive. While animal models replicate important aspects of muscle diseases such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD), the glycoproteins on animal cells differ from those of human cells. These differences may mean that mouse models of DMD do not completely represent the disease that affects people, Baum says.
The precise functions of many of the different glycoproteins on human muscle cells are unknown. Baum’s research will include characterizing the entire set of human muscle glycoproteins, determining the function of a subset of them, and screening for compounds that improve muscle function through their effect on these glycoproteins.
Because she is interested in human-specific glycoproteins, Baum will be studying human cells derived from skin biopsies of boys with DMD and their parents. She will “reprogram” these cells in the lab to become muscle cells, which can then be used for drug screening.
“By using these human muscle cells to screen drug libraries to identify compounds that improve cell function, our aim is to rapidly target therapeutic agents that will be efficacious in patients with Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies,” Baum says.
Her results also may be applicable for individuals who have forms of congenital muscular dystrophy, such as Walker-Warburg syndrome, that result from defects in cellular glycosylation (the process of creating glycoproteins).
Funding for this MDA grant began Feb. 1, 2013.
Grantee: BMD, DMD - Linda Baum, M.D., Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Summer 2013 - ALS — James Shorter, Ph.D.
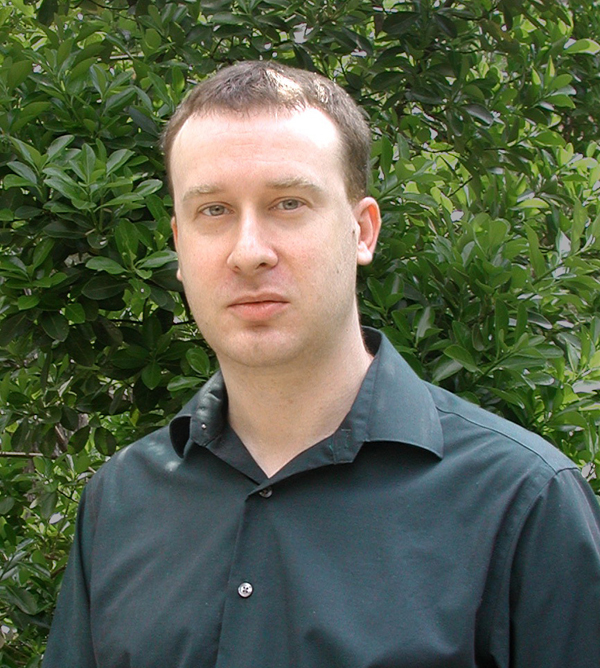

James Shorter, associate professor of biochemistry and biophysics at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $300,000 over a period of three years to develop an experimental approach targeted at protein aggregates in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
In almost all cases of ALS, aggregates or “clumps” of protein accumulate in motor neurons, which may contribute to the death of these cells. Shorter is exploring the possibility that disaggregating [breaking apart] these proteins and returning them to their normal state may be therapeutic. “Unfortunately, mammalian cells have limited ability to disaggregate and renature [properly refold] proteins,” Shorter says, so he employs an enzyme from yeast, called Hsp104.
Shorter is planning to generate variants of the Hsp104 protein that are even more active at breaking up aggregates of the various proteins known to be involved in ALS, including TDP43, FUS and SOD1. After generating such variants, he will test their abilities in yeast and fruit flies, another standard lab model.
“Hsp104-based disaggregases [enzymes that break up aggregates] likely hold great potential as ALS therapeutics,” he says, “as well as for unraveling the role of protein aggregation in ALS pathogenesis.”
Funding for this MDA grant began August 1, 2013.
Grantee: ALS — James Shorter, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant – Winter 2013 – ALS, IBM - Hong Joo Kim, Ph.D.

Hong Joo Kim, a postdoctoral fellow at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tenn., was awarded an MDA development grant totaling $180,000 over a period of three years to study new genes for a newly recognized disorder called multisystem proteinopathy (MSP).
MSP causes symptoms that are seen frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and Paget’s disease of bone (PDB), and in two diseases covered by MDA — amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and inclusion-body myositis (IBM). “Patients with this rare, inherited multisystem disease may experience isolated IBM, FTD, ALS or PDB, which can be indistinguishable from other familial and sporadic cases of these disorders, or the disease may manifest in multiple tissues in the same patient,” Kim says.
While a gene has been discovered that causes MSP, this gene is not responsible for the disease in other families. That led Kim and colleagues to use modern gene-hunting techniques to search for other potential candidates.
They found two such genes, called heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPA2B1 andhnRNPA1), which bind to a cellular messenger called RNA. Alterations in binding and transport are increasingly seen as likely causes of multiple diseases in the nervous system. “Studying the genes that cause this rare multisystem syndrome represents a unique opportunity to identify a fundamental molecular defect that underlies multiple common age-related diseases,” Kim says.
The disease-causing mutations they have found appear to increase the likelihood that individual units of protein will clump together, a feature of many other neurodegenerative diseases. Kim plans to generate fly and mouse research models that contain either the normal or mutant forms of hnRNPA2B1 and A1, in order to study their effects. “We seek to recapitulate the full spectrum of MSP, to elucidate the molecular mechanism of pathogenesis, and to identify target genes that are misregulated in hnRNPA2B1- and A1-associated diseases,” she says, which may lead to new strategies for treating MSP and other diseases.
Funding for this MDA grant began Feb. 1, 2013.
Grantee: ALS, IBM - Hong Joo Kim, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant – Winter 2013 – ALS, IBM - Eric Ross, Ph.D.
Eric Ross, associate professor of biochemistry and molecular biology at Colorado State University in Fort Collins, was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $363,000 over a period of three years to study proteins whose aggregation causes neurodegeneration.
Neurodegenerative diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), are characterized by the formation of protein clumps, or aggregates, in or around muscle-controlling nerve cells called motor neurons. Aggregates also are seen in the muscle disease inclusion-body myositis (IBM). These aggregates are believed to indicate an ongoing toxic process within the cell and may be toxic themselves.
“Interestingly, similar protein aggregation can be seen even in simple single-cell organisms such as yeast,” says Ross. Some aggregates can harm not only the cell in which they form, but also neighboring cells by spreading to them and inducing aggregation. Such proteins are called prion-like for their resemblance to proteins found in prion diseases like bovine spongiform encephalopathy (mad cow disease).
Yeast makes a powerful model system in which to study the spread of prion-like proteins, Ross says, because it grows rapidly and its genes can be easily manipulated. “Based on studies in yeast, our lab has developed methods to identify new disease-associated proteins in other organisms. Remarkably, in just the past few years, various labs have linked mutations in six of these proteins to certain inclusion-body myopathies and some forms of ALS.”
Ross will be examining how the sequence of amino acids in these proteins affects aggregation and toxicity, and how disease-associated mutations change the physical properties of the proteins.
“These studies will provide insight into the causes of these diseases, facilitate the identification of potential drug targets for therapeutic intervention, and improve our ability to identify other disease-associated prion-like proteins,” he says.
Funding for this MDA grant began Feb. 1, 2013.
Grantee: ALS, IBM - Eric Ross, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant – Winter 2013 – ALS, IBM - Benoit Coulombe, Ph.D.
Benoit Coulombe, director of the Proteomics and Gene Transcription Laboratory at the University of Montréal in Quebec, Canada, was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $377,067 over a period of three years to study the regulation of a protein whose gene, when mutated, can cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and inclusion-body myositis (IBM).
Valosin Containing Protein (VCP) helps clear misfolded proteins so that they do not cause damage within cells. Mutations in the VCP gene that interfere with this function are one cause of both ALS and IBM.
VCP is a type of protein called a molecular chaperone. “Building a detailed understanding of the mechanisms by which molecular chaperones play a role in the onset and development of neuromuscular disorders is important for the design of new tools to better diagnose and treat some of these conditions,” Coulombe says.
Recently, his group discovered that a set of proteins called methyltransferases regulates the activity of VCP, raising the possibility that this regulatory system may go awry when VCP is mutated. By studying the activity of methyltransferases and VCP in both healthy and diseased cells, Coulombe hopes to learn more about the regulation of chaperones and how it is affected by disease-causing mutations.
The goal is to examine the full range of changes brought about by methyltransferase activity, using state-of-the-art tools to capture and characterize the set of protein modifications in cells. Coulombe also will explore whether changes in VCP and the proteins with which it interacts can serve as a “biomarker,” helping to identify diseased cells and following their response to treatment.
“Characterizing these newly discovered enzymes will help us understand the molecular bases of these disorders and accelerate the development of diagnosis and therapeutic tools relevant to their treatment,” he says.
Funding for this MDA grant began Feb. 1, 2013.
Grantee: ALS, IBM - Benoit Coulombe, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant – Winter 2013 – ALS, CMT - Martha Bhattacharya, Ph.D.
Martha Bhattacharya, a postdoctoral research scholar in developmental biology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Mo., was awarded an MDA development grant totaling $180,000 over a period of three years to study how and why axons degenerate.
Axons are the long extensions of motor neurons (muscle-controlling nerve cells) that link up with muscles. Signals are sent down the axon to cause the muscle to contract. When an axon degenerates, it can no longer carry those signals, leading to weakness.
“In neuromuscular diseases where motor neuron dysfunction is the primary cause of disability, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease, axonal degeneration is a unifying pathological hallmark of disease progression,” Bhattacharya says.
To study axonal degeneration, she and her colleagues developed a fruit fly research model that allows the identification of necessary components of the axonal degeneration cascade. Using this system, she has identified several key steps in the process, including one involving a protein called G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR), and another called protein kinase.
“These receptors are highly desirable drug targets,” Bhattacharya says, and pharmaceutical companies have a great deal of experience designing drugs to influence their behavior. “For the GPCR, we will determine its signaling mechanism in mammalian neurons and test its ability to protect neuromuscular synapses after injury. For the kinase, we will examine the effects of loss of this protein on mouse axons and synapses,” the sites of information exchange between nerve and muscle.
Learning more about the details of axonal degeneration also will help researchers understand more about the entire disease process, potentially leading to other targets for therapeutic intervention.
Funding for this MDA grant began Feb. 1, 2013.
Grantee: ALS, CMT - Martha Bhattacharya, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Additional Grants 2013 - ALS — ALS Therapy Development Institute (ALS TDI)

MDA and the nonprofit biotech ALS Therapy Development Institute (ALS TDI) have extended their strategic research partnership through 2013. With the extension comes a $3.2 million MDA grant to help support the nonprofit biotech's continued progress toward developing treatments for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
ALS TDI, located in Cambridge, Mass., screens at least 25 potential ALS therapeutics every year.
“MDA has been, and continues to be a key partner in providing us the resources needed to move more ideas and projects forward faster than before,” said Steve Perrin, ALS TDI CEO and chief scientific officer. “MDA support has enabled many discoveries and advancements which hold great potential for people diagnosed with ALS.”
Grantee: ALS — ALS Therapy Development Institute (ALS TDI)
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Summer 2015 - SMA - Kevin Foust, Ph.D.

Kevin Foust, assistant professor in the department of neuroscience at Ohio State University in Columbus, was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $293,378 over three years to investigate disruption of gut bacteria in spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). The gut microbiome is the collection of organisms that inhabit a healthy gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Dysbiosis, or changes in the gut microbiome, disrupts GI motility, nutrient uptake and lipid metabolism, creating a spiral that impacts patient health. Foust will examine the microbiome in mouse models of SMA and determine the effects of antibiotics, probiotics and fecal transplants on the SMA mouse microbiome. This study may help guide patients in the use of probiotics or other measures in order to maintain normal gastrointestinal function and nutritional health.
Funding for this MDA research grant began Aug. 1, 2015.
Grantee: SMA - Kevin Foust, Ph.D.
Grant type: Research Grant
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Summer 2015 - SMA - Constantin d’Ydewalle, Ph.D.

Constantin d’Ydewalle, a postdoctoral fellow at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore was awarded an MDA development grant totaling $180,000 over three years to test a gene therapy designed to increase levels of SMN protein in spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). The work, co-funded by the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine Foundation for Research and Education (AANEM), may lead to the development of a new treatment that could be useful by itself or in combination with other therapies in development.
Funding for this MDA development grant began Aug. 1, 2015.
Grantee: SMA - Constantin d’Ydewalle, Ph.D.
Grant type: Development Grant
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant – Winter 2013 – ALS - Xin Wang, Ph.D.
Xin Wang, assistant professor of neurosurgery at Harvard Medical School in Boston, Mass., was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $405,000 over a period of three years to identify and test novel drug candidates for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
The need for new drugs in ALS is clear, Wang says, because the only drug approved for the disease is riluzole, which extends survival on average by only about three months.
Preliminary evidence suggests that increased cellular signaling of the melatonin system may be neuroprotective. Melatonin, a hormone secreted by the pineal gland, binds to the melatonin receptor 1A (MT1). Wang will test the hypothesis that increased stimulation of MT1 will slow disease development and progression. Her work will involve identifying compounds called MT1 agonists that bind to and stimulate the receptor. She will then test these agonists in cell culture and in a mouse model of ALS.
Funding for this MDA grant began Feb. 1, 2013.
Grantee: ALS - Xin Wang, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Summer 2015 - SMA - Arthur Burghes, Ph.D.

Arthur Burghes, professor of biological chemistry and pharmacology, molecular genetics, and neurology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $188,613 over two years to refine how a genotype can be used to predict the severity of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Burghes will develop assays to test whether SMA patients have either intact or defective SMN2 genes, which serve as the backup for the SMN1 gene lost in SMA patients. Since the level of SMN2 determines the disease severity in SMA patients, these assays may be able to better predict how disease may progress in an individual.
Funding for this MDA research grant began Aug. 1, 2015.
Grantee: SMA - Arthur Burghes, Ph.D.
Grant type: Research Grant
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant – Winter 2013 – ALS - Sunitha Rangaraju, Ph.D.

Sunitha Rangaraju, a postdoctoral research scientist at the Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, Calif., was awarded an MDA development grant totaling $180,000 over a period of three years to determine whether compounds that slow certain aspects of aging may be therapeutic in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
The biggest known risk factor for ALS is advancing age, suggesting that the processes that contribute to aging also may contribute to ALS. This led Rangaraju and colleagues to hypothesize that compounds that slow the aging process might be valuable as drugs against ALS. To that end, their lab screened more than 89,000 molecules for those that delay aging and extend life span in C. elegans, a small worm that is widely used to study aging.
That screen turned up more than 100 molecules that extend worm life span. Rangaraju is now testing those compounds in a worm model of ALS to see if they also contribute to longevity in the context of the disease.
The worm research model of ALS shares important characteristics with human ALS, including “protein aggregation, movement defects, reduction of neuron-to-muscle signals and a shorter life span,” Rangaraju says. She already has identified several compounds that extend life span in these worms, and now will test others, and determine how the most promising ones influence protein aggregation or other aspects of ALS. She then plans to test the most promising molecules in mouse models of ALS, the next step in drug development.
“In the field of ALS, great progress has been made in developing animal models of the disease and unraveling disease mechanisms,” says Rangaraju. “These findings allow us to test novel strategies to develop therapeutic molecules to ameliorate the disease.”
Funding for this MDA grant began Feb. 1, 2013.
Grantee: ALS - Sunitha Rangaraju, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Summer 2015 - SBMA - Diane Merry, Ph.D.

Diane Merry, associate professor at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia, was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $300,000 over three years to identify therapeutic opportunities to promote normal androgen receptor function while preventing the toxic effects of polyglutamine expansion in spinal-bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA). Working with GlaxoSmithKline, Merry will test small molecule compounds that activate an enzyme called SIRT1 in cell and mouse models of SBMA to determine their therapeutic potential.
Funding for this MDA research grant began Aug. 1, 2015.
Grantee: SBMA - Diane Merry, Ph.D.
Grant type: Research Grant
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
Grant - Summer 2015 - Muscle disease - Michael Kyba, Ph.D.

Michael Kyba, at the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis, was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $300,000 over three years to study the role of satellite cells in skeletal muscle regeneration. Kyba’s research to discover and study genes that regulate the regenerative potential of satellite cells will lead to a better understanding of skeletal muscle regeneration, with implications for our understanding of skeletal muscle regeneration in disease states and of the differences in muscle regenerative potential between individuals.
Funding for this MDA research grant began Aug. 1, 2015.
Grantee: Muscle disease - Michael Kyba, Ph.D.
Grant type: Research Grant
Award total:
Institution:
Country:
MDA Resource Center: We’re Here For You
Our trained specialists are here to provide one-on-one support for every part of your journey. Send a message below or call us at 1-833-ASK-MDA1 (1-833-275-6321). If you live outside the U.S., we may be able to connect you to muscular dystrophy groups in your area, but MDA programs are only available in the U.S.