Darren Monckton, professor of human genetics at the University of Glasgow in Scotland, was awarded an MDA research grant totaling $273,892 over a period of two years to develop new diagnostic tests for myotonic muscular dystrophy type 1 (MMD1, also known as DM1)
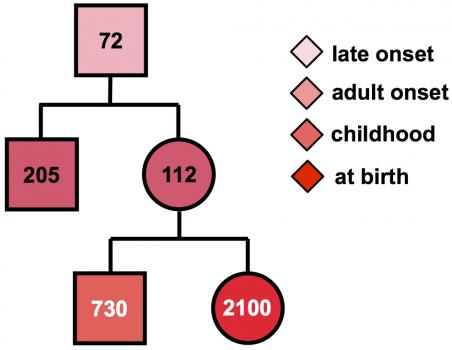
MMD1 is caused by expansion of part of the DNA code in the DMPK gene. Normally, this gene has a small number of repeats of the DNA “letters” CTG. But in people with MMD1, the number of repeated CTG units is 50 or more, and can be over 1000. Furthermore, the number of repeated units in the genes can grow over the lifetime and may differ between different cells.
“In the standard diagnostic test, this genetic instability is ignored,” Monckton says, “and only an average number of repeats is measured.” But the variation may contain important clues to when the disease is likely to begin, and so may provide valuable information to families and individuals with the MMD1 repeat about the future course of disease.
“Using specialized research techniques, we can measure the number of CTG repeats in many cells, then use a computer model to calculate the number of CTGs the patient had at birth,” Monckton notes. “This number much more accurately predicts when symptoms are likely to start. In addition, the CTGs are sometimes interrupted by other groups of three letters, such as CCG, usually leading to milder symptoms,” and later onset in future generations. “Unfortunately, the current genetic test does not take account of age-dependent changes in the number of repeats or detect the presence of these interruptions.”
Monckton will collaborate with genetic testing laboratories to develop new diagnostic tests that will allow the detection of both these important features. In addition to benefits for individual families, the new tests should help make the interpretation of clinical trial results more accurate, since any effects of treatment can be measured against the severity of the genetic mutation.
Funding for this MDA grant began Feb. 1, 2013.
Grantee: MMD - Darren Monckton, Ph.D.
Grant type:
Award total:
Institution:
Country: